01. July, 2025delish0
Ribbon slitting machine is a precision equipment used to cut wide ribbon (thermal transfer material) into a specific width, and its high-precision slitting depends on the collaborative optimization of mechanical design, control system and process parameters. Here's how it works and how to achieve high-precision slitting:

First, the core composition of the ribbon slitting machine
1. Unwinding system
◦ Constant tension control, through the magnetic particle brake or servo motor to dynamically adjust the unwinding speed to avoid material stretching deformation.
◦ Equipped with an EPC device, the edge position is detected by a photoelectric sensor, and the transverse position of the coil is adjusted in real time (the accuracy can reach ±0.1mm).
2. Slitting unit
◦ Round knife slitting: High hardness alloy round knife (hardness HRC60 or above) is matched with the bottom roller, and the knife pressure is controlled by pneumatic or servo pressure.
◦ Laser slitting (high-end model): non-contact cutting of laser head, suitable for ultra-thin ribbons (such as 3μm), no flash.
3. Winding system
◦ Independent servo motor drives the winding shaft, using taper tension control (the initial tension is large, and gradually decreases with the increase of the winding diameter).
◦ Equipped with surface take-up or center take-up mode to ensure that the web is flat and wrinkle-free.

Second, the key technology of high-precision slitting
1. Dynamic tension control
◦ PID closed-loop control is adopted, and the unwinding/rewinding torque is adjusted in real time through the tension sensor feedback, and the tension fluctuation range can be controlled within ±5%.
◦ Segmented tension setting: Adjust the tension parameters according to the ribbon material (such as wax-based, mixed-based, resin-based).
2. Tooling system optimization
◦ Tool angle: The round blade angle is usually 30°~45°, and the blade life can reach more than 1000km.
◦ Tool runout control: the radial runout of the spindle ≤0.005mm to avoid the fluctuation of slitting width.
◦ Online sharpening system: Some equipment is equipped with automatic sharpening device to maintain the sharpness of the cutting edge.
3. Slitting width control
◦ High-precision guide roller: straightness ≤ 0.01mm/m to ensure that the ribbon has no lateral offset.
◦ CNC tool adjustment system: servo motor drives the toolholder to move, with a resolution of up to 0.01mm (such as Mitsubishi servo system).
◦ Visual inspection: CCD camera monitors the slitting edge in real time, and adjusts the tool distance (optional function).
4. Environmental control
◦ Clean room (Class 1000) to reduce dust adhesion.
◦ Stable temperature and humidity (23±2°C, RH50±5%) to prevent the ribbon from being deformed by moisture.
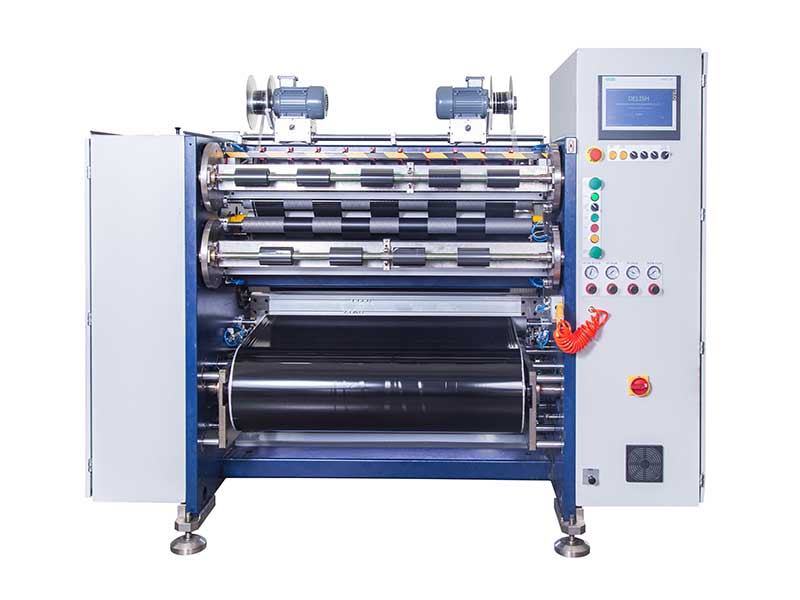

Third, influence of process parameters
| parameter | Typical | Adjustment principles |
| Slitting speed | 50-300m/min | Speed ↑ needs to be synchronized to improve the tension control response |
| Knife press | 0.2-0.8MPa | Resin-based ribbons require higher knife pressure |
| Slitting width tolerance | ±0.05mm (high-end) | Laser slitting is required when the width ≤ 1mm |
| Winding hardness | 70-90ShoreA | Too hard can lead to interlaminar penetration of the ribbon |
Fourth, solutions to common problems
• Flash/flash: Check for tool wear or insufficient tool pressure, and replace the ceramic-coated round knife to increase the life by 30%.
• Coil wrinkling: Adjust the winding taper curve to increase the wrapping angle of the flattened roll (recommended ≥ 45°).
• Width out-of-tolerance: Calibrate the parallelism of the guide rollers and check the resolution of the servo drive encoder (≥ 17 bit).
Fifth, cutting-edge technology trends
1. AI adaptive control: Optimize the combination of tension/velocity parameters through machine learning to reduce test waste.
2. Nano Coated Tools: Diamond-like (DLC) coating can extend tool life by up to 3 times conventional ones.
3. Digital twin system: virtual debugging predicts the slitting effect in advance, shortening the changeover time by more than 50%.
Through the integration of the above technologies, the modern ribbon slitting machine can achieve a slitting accuracy of ±0.02mm, which meets the needs of high-end applications such as RFID tags. In the actual selection, the equipment level needs to be matched according to the thickness of the ribbon substrate (commonly 4.5-12 μm) and the capacity requirements.
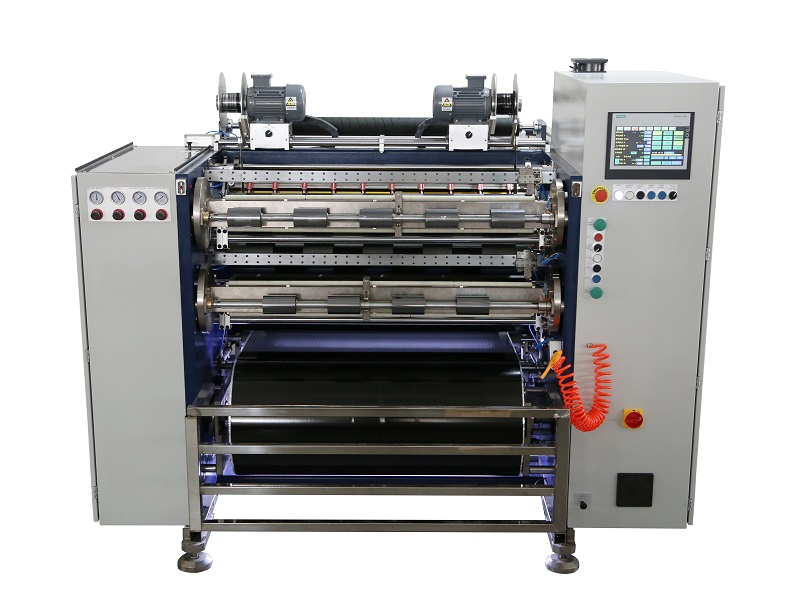




 Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus
Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus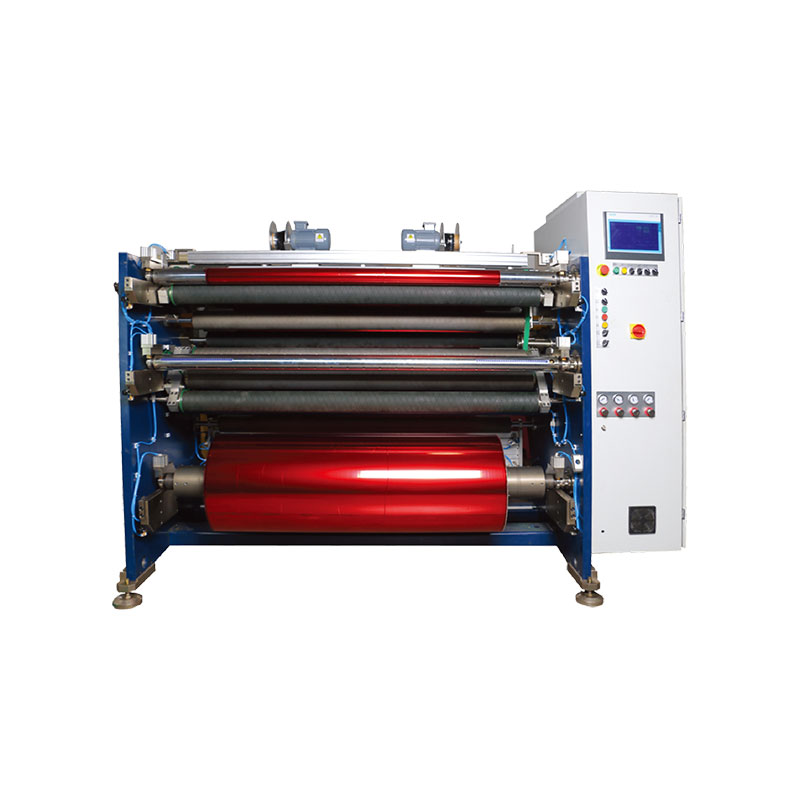 Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm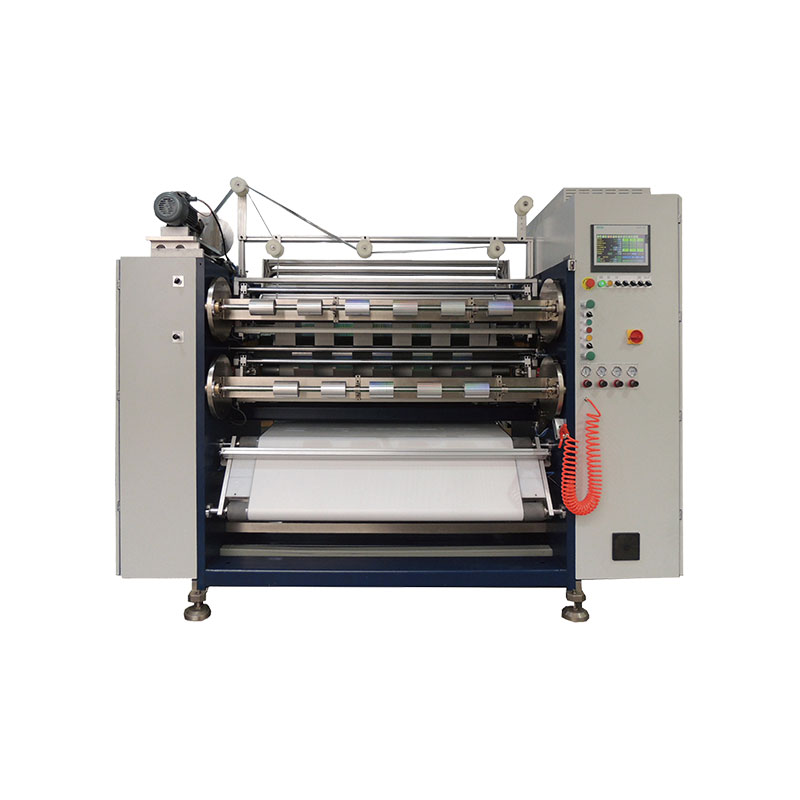 Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts)
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts)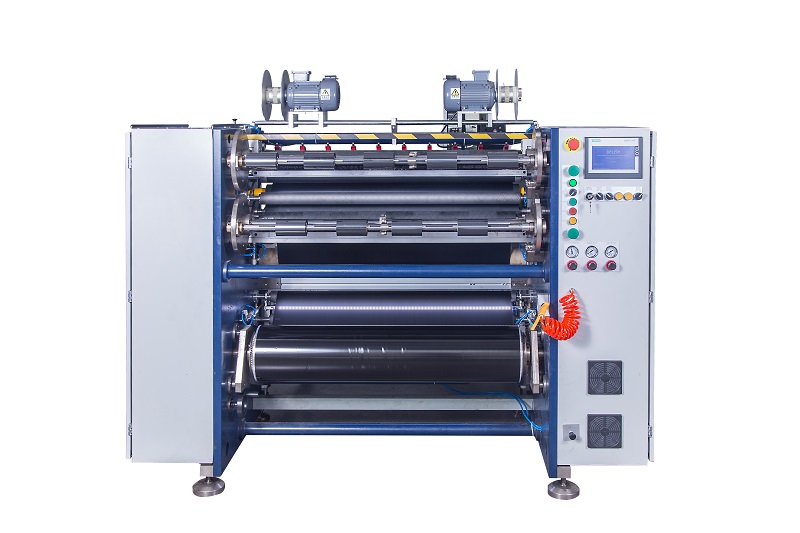 Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus
Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus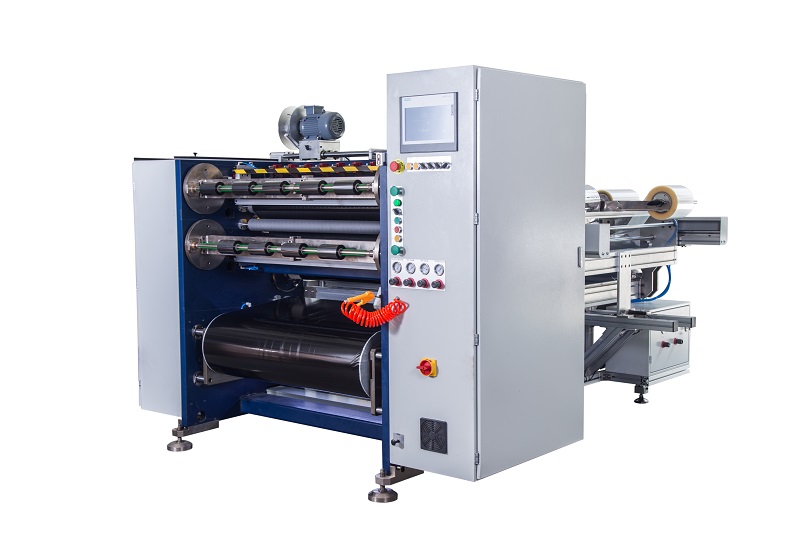 Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus
Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus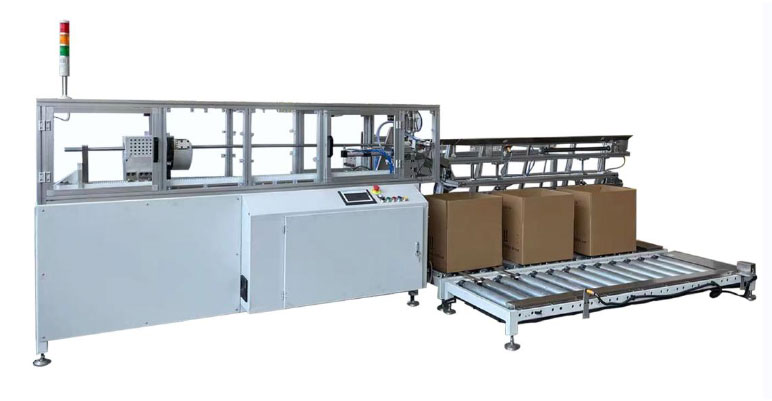 Auto Paper Core Cutter
Auto Paper Core Cutter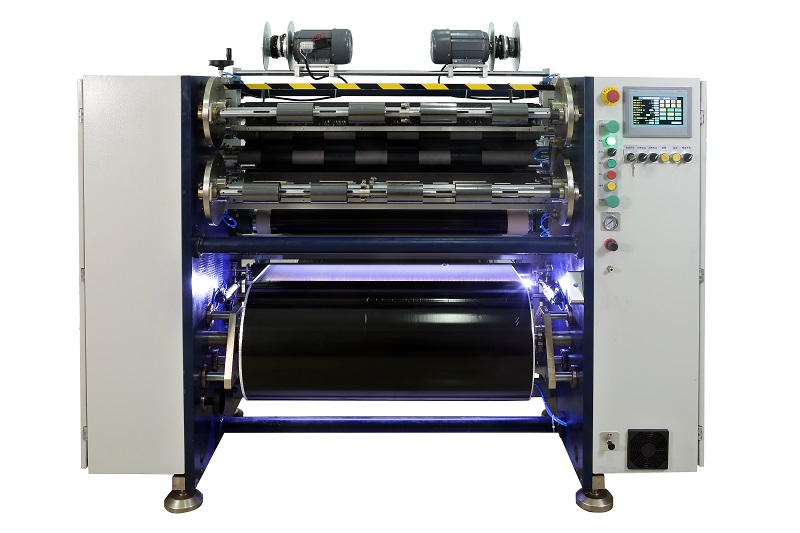 Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2
Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2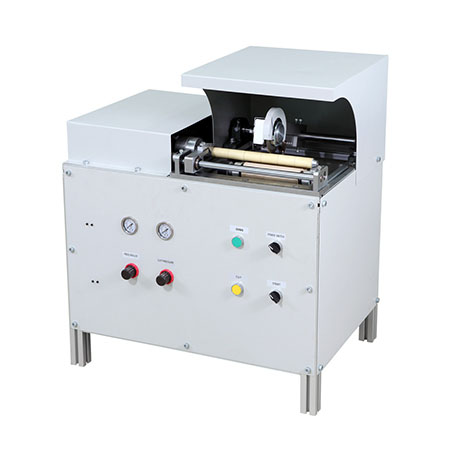 Manual Paper Core Cutter
Manual Paper Core Cutter