21. August, 2025delish0
In the context of modern manufacturing pursuing high efficiency, high quality and flexible production, the automation upgrade of traditional slitting machines has become the only way for enterprises to improve their competitiveness. In this transformation process, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) play an irreplaceable key role in their core control functions and refined parameter settings, as the "brain" of the entire system. Together, they transform a simple mechanical device into an intelligent, precise, and stable high-performance production facility.
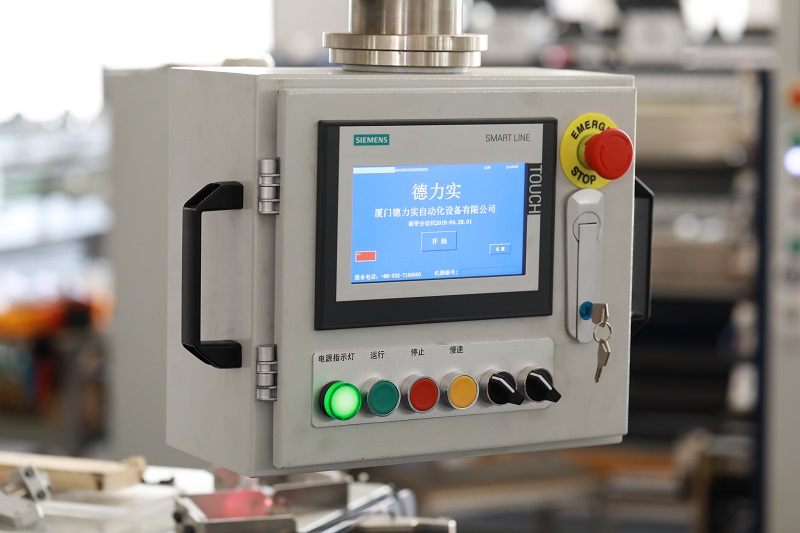

1. Limitations and upgrade requirements of traditional slitting machines
Traditional slitting machines, such as those with mechanical drives, relay control, or simple microcontrollers, are commonly associated with the following problems:
• Low efficiency: the order change speed is slow, and the adjustment relies on the experience of the master, which is time-consuming and consuming.
• Poor accuracy: The tension control is unstable, which is prone to problems such as snaking, wrinkling, and material breakage, and the yield is low.
• Insufficient flexibility: difficult to adapt to different materials, different widths and diameters of coils.
• Low degree of informatization: lack of production data recording, fault diagnosis, and remote monitoring functions.
• Difficult maintenance: The relay line is complex and troubleshooting.
The core goal of automation upgrades is to solve these problems through electrical transmissions and computer control, and PLCs are the cornerstone of achieving this goal.
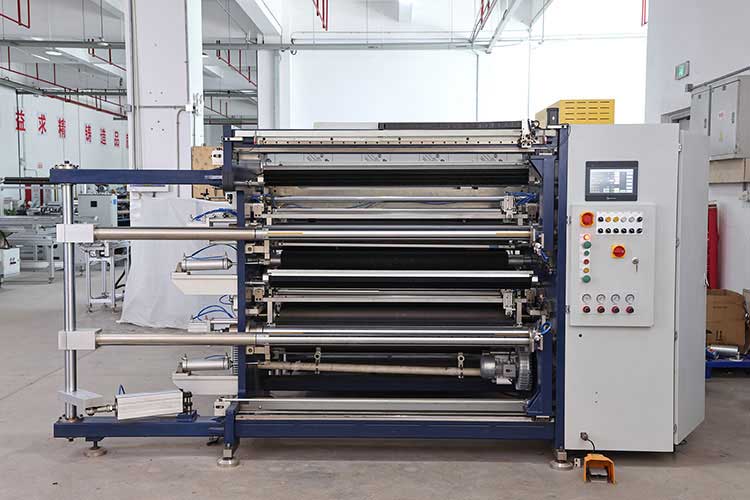

2. The core role of PLC in the automation upgrade of the slitting machine
PLC is no longer just a simple logic controller that replaces relays, it has evolved into a comprehensive platform integrating logic control, motion control, and process control.
1. Central command and coordination center
PLC is the core of the entire slitting machine control system. It receives instructions and signals from the human-machine interface (HMI) and various sensors (such as correction EPC, tension sensor, encoder), and outputs control commands to the actuator (such as servo/variable frequency motor, pneumatic components, solenoid valves) through logical operation and processing of internal programs, and coordinates the orderly and synchronous work of various units such as unwinding, traction, slitting, and winding.
2. High-precision tension control
Tension control is the soul of the slitting machine and directly affects the quality of the slitting machine. By integrating advanced PID control algorithms, PLC processes the feedback signal of the tension sensor in real time, dynamically adjusts the torque or speed of the unwinding and rewinding servo motors, and realizes constant tension or taper tension control. This is essential for handling extremely thin films, stretchable fibers, or heavy papers, effectively avoiding material pulling or sagging and wrinkling.
3. Precise synchronous motion control
Modern slitting machines often employ multi-servo systems. PLC controls multiple servo drives via high-speed buses (e.g., EtherCAT, Profinet) to achieve precise electronic cam synchronization between axes. For example, the winding shaft must automatically adjust the speed as the roll diameter increases to keep the linear speed constant, and the cutter shaft needs to be strictly synchronized with the material feed rate to ensure a neat cut. All this is precisely calculated and executed by the motion control function block inside the PLC.
4. Automatic order change and recipe management
This is the key to improving efficiency. Operators can preset "Recipes" for different products on the HMI, including:
◦ Slitting width
◦ Slitting length/quantity
◦ Tension setpoint
◦ Retract taper
◦ Speed parameters
When changing orders, call the corresponding recipe with one click, and the PLC will automatically drive the servo motor to move the tool holder to the specified width, and set all the operating parameters, which greatly reduces the adjustment time and the skill dependence on the operator, and realizes the flexibility of production.
5. Integrated safety controls
PLC can integrate safety modules (or connect safety relays through safety buses) to process signals from safety equipment such as emergency stop buttons, safety light curtains, and area sensors, and realize safe shutdown functions that meet safety levels (such as SIL2/PLd) to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
6. Data collection and communication networking
As an information node, PLC can collect and record equipment operating status, output, fault alarm and other data in real time, and upload these data to SCADA system or MES (manufacturing execution system) through industrial Ethernet to realize factory-level data visualization and production management, laying the foundation for digital factories.
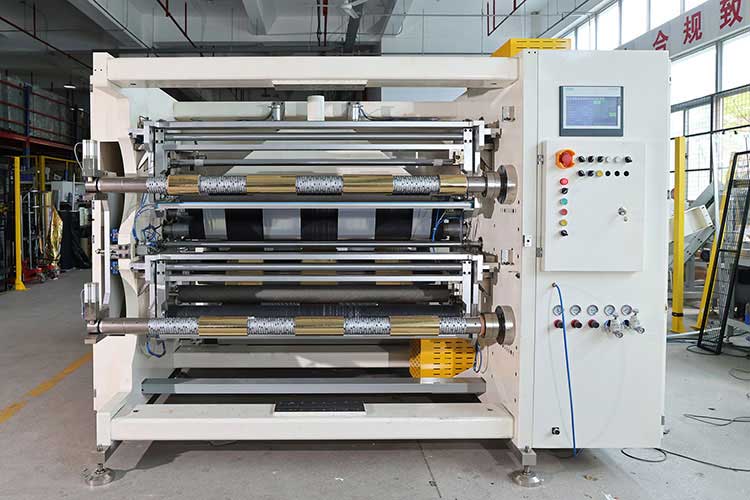

3. Parameter setting: transform PLC functions into a bridge for actual productivity
No matter how powerful the PLC is, it needs the right parameters to drive. Parameter setting is the process of "translating" process requirements into machine-executable commands, and the degree of refinement directly determines the final production effect.
Key parameter categories include:
• Mechanical parameters: such as transmission ratio, roller diameter, encoder line number, etc., these are the basis for PLC to perform precise position and speed calculations.
• Tension parameters:
◦ Initial tension setpoint: Set according to different material properties (e.g., PP, PET, aluminum foil).
◦ PID parameters (scale, integral, differentiation): The tuning of these three parameters directly determines the response speed, stability, and anti-interference ability of tension control. The commissioning engineer needs to make fine adjustments according to the site conditions.
◦ Taper coefficient: controls the curve of the tension decreasing with the increase of the coil diameter during winding, to prevent the core from being crushed or the outer material from slipping.
• Speed parameters: including acceleration and deceleration time (S-curve), maximum running speed, etc., smooth acceleration and deceleration are conducive to reducing the impact on the material and ensuring smooth start and stop.
• Guidance Correction (EPC) Parameters: Controls the sensitivity and response speed of the guiding sensor and actuator to ensure that the edge or centerline of the material is always aligned.
• Axis parameters: For circular knife slitting, the amount of cutter overlap, cutting depth, etc. need to be set; For knife slashing and slitting, it is necessary to accurately calculate the phase synchronization between the flying cutter and the bottom cutter.
The value of parameter setting: Excellent parameter setting can give full play to the hardware performance of the equipment, find the best balance between speed, accuracy and stability, and is the "secret" to achieve high-quality and efficient production.
4. Summary
The automation upgrade of the slitting machine essentially transforms it from a "mechanically driven" device to a "software-defined" intelligent device. In this transition:
• PLC provides the hardware foundation and capability platform for complex control, high-precision motion, and intelligent decision-making.
• Parameter setting is the "soul" and "knowledge" injected into the platform, which carries the specific production process and operating experience.
The two complement each other and are indispensable. Only by investing in a powerful and open PLC system, supplemented by in-depth and meticulous parameter optimization and process research, can enterprises truly unleash the full potential of the slitting machine, and ultimately obtain significant returns in quality, efficiency and cost control, and win market advantages.






 Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus
Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts)
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts) Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus
Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus
Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus Auto Paper Core Cutter
Auto Paper Core Cutter Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2
Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2 Manual Paper Core Cutter
Manual Paper Core Cutter