03. September, 2025delish0
With the advancement of the global "plastic ban" and the improvement of environmental awareness, the application of degradable films (such as PLA, PBAT, PBS, PHA, etc.) is becoming more and more widespread, but its slitting processing does pose a new challenge to traditional processes.
New trend of environmentally friendly film slitting
Traditional slitting focuses on efficiency, precision, and rewinding quality. The new trend of environmentally friendly film slitting revolves around two cores: "material properties" and "sustainability":
1. Refined and customized processing: With diverse customer needs, slitting factories need degradable films that can handle different thicknesses and materials (even multi-layer co-extrusion) to provide high-precision narrow slitting and complex devolving solutions.
2. Intelligent and data-driven: Utilize IoT sensors and AI algorithms to monitor tension, pressure, temperature and other parameters during the slitting process in real time, optimize the process through big data analysis, and reduce quality fluctuations caused by human factors, especially suitable for performance-sensitive degradable materials.
3. Low-carbon and energy-saving production: The slitting equipment itself is developing in the direction of low energy consumption and high efficiency. At the same time, the process is optimized to reduce waste generation, and the leftovers generated during the slitting process are recycled and reused (such as biodegradation or physical recycling) to achieve a green closed loop in the production process.
4. Clean and pollution-free throughout the process: emphasize the cleanliness of the production environment and avoid dust, oil and other pollution films, which are crucial for degradable films for medical and food packaging with high cleanliness requirements.

Core challenges: the characteristics of degradable materials and their slitting difficulties
The reason why degradable materials are difficult to cut is that their physical properties are significantly different from traditional PE, BOPP and other plastics:
1. Large differences in mechanical properties:
◦ Low toughness and brittleness: PLA (polylactic acid), for example, is harder and more brittle than traditional plastics, lacking ductility. Under slitting tension, edge cracking, microcracking and other problems are more likely to occur.
◦ Poor tear resistance: If the slitting blade is not sharp, it is very easy to cause tearing, rather than a smooth cut.
2. High Heat Sensitivity:
◦ The glass transition temperature and melting point of degradable materials are generally lower. The heat generated by the friction between the blade and the film during the slitting process can easily soften and melt, leading to knife sticking. The molten material can adhere to the blade, causing uneven sections, drawing and residue, and contaminating the film roll.
3. Coefficient of Friction (COF) Instability:
◦ The smoothness of the degradable film may be uneven, or change during use (affected by temperature and humidity), which brings great difficulties to the tension control during slitting and winding, and can easily lead to problems such as uneven winding (winding) and collapse.
4. Prominent static electricity problem:
◦ Degradable materials are generally good insulators and are prone to generating a lot of static electricity. Static electricity can cause the film to absorb dust, make it difficult to wind neatly, and even cause safety production problems.
5. Age-sensitive (aging) issues:
◦ The properties of some materials will change during storage (e.g., PLA embrittlement), which requires the slitting process to be dynamically adjusted according to the incoming batch and even the storage time.

How to address these challenges? Systemic solutions
To address the slitting challenges of degradable materials, it is necessary to systematically upgrade and optimize from four aspects: equipment, process, blade, and environment.
1. Equipment Upgrades: Tailored for soft and tough, brittle and sticky materials
1. High-precision tension control system:
◦ Adopt a fully automatic digital tension control system with taper tension and torque decay control functions. Adopt a large tension at the beginning of slitting and gradually reduce the tension as the roll diameter increases, avoiding the inner film crushing (especially important for soft PBAT) or edge cracking (important for brittle PLA) caused by "tighter rolling".
◦ Magnetic powder clutch or servo motor drive is recommended for millisecond response and precise control of tension.
2. Dedicated Slitting Knife Holder Design:
◦ Low-temperature slitting: Cooled tool holder or air cooling system is used to blow cold air near the blade, effectively reducing the blade temperature and fundamentally solving the problem of material melting and sticking knives.
◦ Tool Selection:
▪ Single-sided blade (razor-style): Better for thin, brittle materials for neat cuts.
▪ Double-sided blade (scissor type): It is more suitable for thick, tough materials and has a smooth cut. However, it requires extremely high installation accuracy.
◦ Teflon or ceramic-coated blades: These coatings have a very low surface and are effective in preventing material from sticking after melting.
3. Efficient Static Elimination Systems:
◦ Install ion air rods or static eliminators at key stations such as unwinding, slitting, and winding to continuously neutralize the static charge on the film surface and ensure that the slitting process is clean, tidy, and safe.
4. Contact Roller Material Upgrade:
◦ The surface of the contact roller (pressure roller) of the winder can be coated with an elastic material such as polyurethane (PU) to provide gentle and uniform pressure to avoid crushing the soft film.

2. Process optimization: parameters are the soul
1. Tension setting:
◦ The principle of "better to be small than big". Fine-tuning is carried out starting from the minimum tension that ensures neat retraction, and sufficient specimen testing must be carried out.
◦ Establish an independent database of tension parameters for products of different materials, different thicknesses, and different widths.
2. Blade Angle and Overlap:
◦ Adjust the angle of the blade (back) and the amount of cut (Overlap). For materials that are easy to stick to knives, appropriately reduce the amount of cutting, and use the method of "sharp angle light cutting" to reduce friction heat.
◦ Maintain the ultimate sharpness of the blade and establish a strict blade replacement and grinding system.
3. Slitting Speed:
◦ Faster is not always better. For difficult-to-cut degradable materials, appropriately reducing the slitting speed is an effective way to reduce heat build-up and ensure the quality of the section.
4. Environmental Control:
◦ Control the temperature and humidity of the workshop. The performance of degradable materials is sensitive to temperature and humidity, and a stable production environment (such as 22±2°C, 50%±5%RH) is the prerequisite for ensuring the stable quality of slitting.
3. Operation and maintenance: details determine success or failure
1. Roll handling and storage:
◦ Degradable film rolls are more "delicate" than traditional plastics, and must be handled gently during handling and storage to avoid edge damage caused by collisions.
◦ Pay attention to storage conditions to prevent moisture absorption or aging of materials.
2. Cleaning and Maintenance:
◦ Keep the equipment, especially the guide rollers, blades, and pressure rollers, absolutely clean, and wipe them regularly with harmless solvents such as alcohol to prevent dust pollution.
summary
Addressing the challenge of slitting degradable materials is essentially a transformation from "experience-driven" to "technology-driven".
• Core Idea: Understand material properties → Adjust equipment configuration → Optimize process parameters → Tightly control the environment.
• Investment Focus: Prioritize upgrading tension control systems, blade cooling systems, and static elimination systems.
• Soft power: Establish a refined process database and standard operating procedures (SOPs) to strengthen employee training on material properties.
With advances in materials science and equipment technology, the slitting of degradable films is becoming more and more mature. Those companies that can take the lead in mastering these new technologies and processes will surely occupy a leading position in the new blue ocean of environmentally friendly packaging.
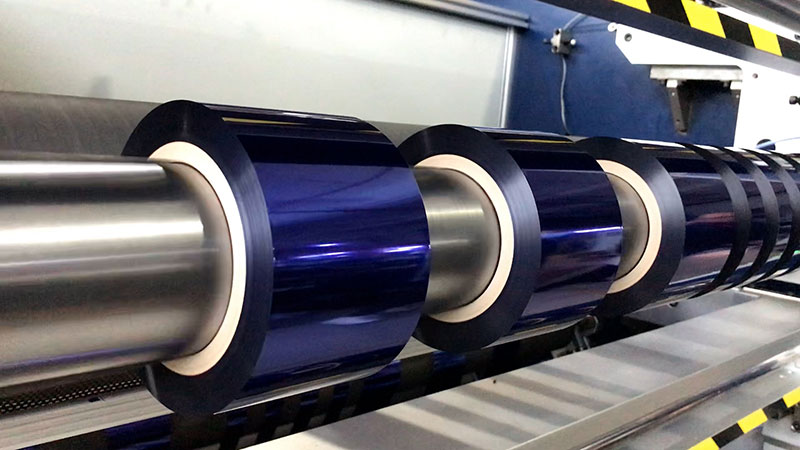
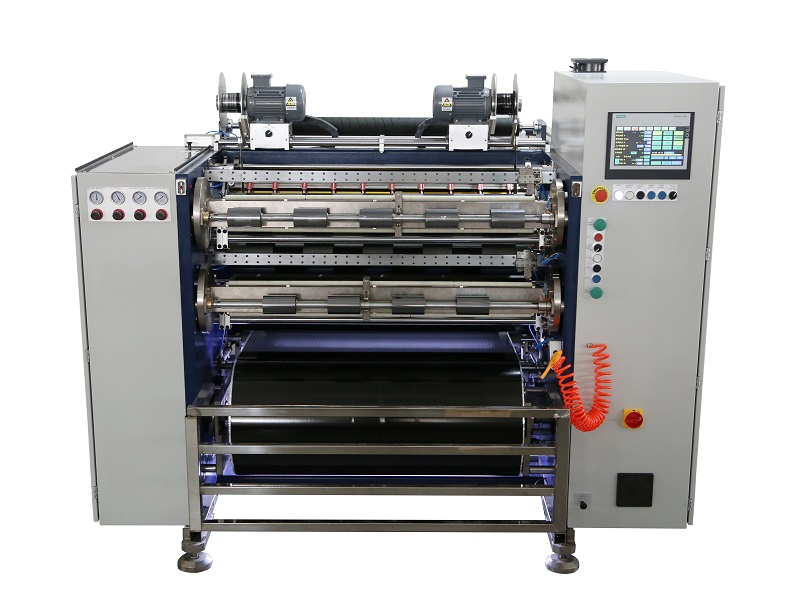





 Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus
Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts)
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts) Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus
Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus
Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus Auto Paper Core Cutter
Auto Paper Core Cutter Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2
Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2 Aluminum Foil Slitting Machine
Aluminum Foil Slitting Machine