27. November, 2025delish0
In many industries such as packaging, printing, lithium batteries, films, non-woven fabrics, etc., slitting machines are indispensable key equipment for the back-end process. A suitable slitting machine is the cornerstone of ensuring product quality and improving production efficiency; A single wrong selection can mean ongoing quality problems, high maintenance costs, and heavy material waste.
Where does the "pit" come from? It often stems from insufficient understanding of the matching of its own material properties with equipment performance. This article will go straight to the core and sort out the key points of slitting machines of different materials for you, helping you accurately avoid pitfalls and make a wise investment.
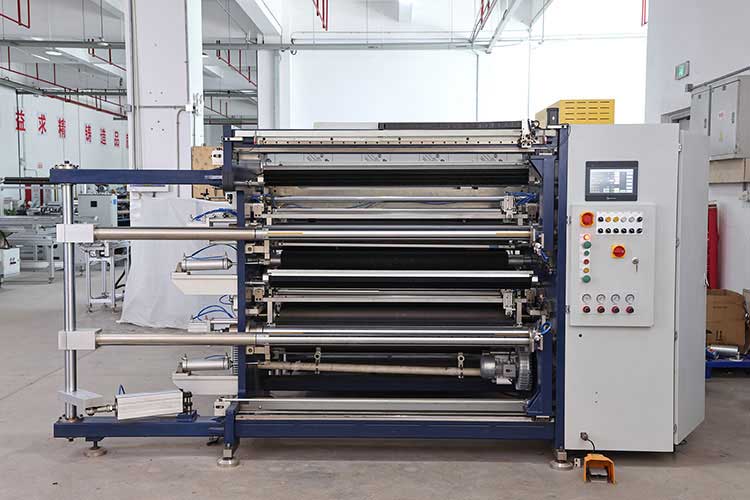

The first step to avoid pitfalls: recognize the "nature" of your material
Before talking about the model, it's essential to have a deep understanding of the material you're going to slit. The characteristics of the material directly determine the technical configuration of the slitting machine.
• Material type: Is it plastic film (e.g., BOPP, CPP, PET), paper, non-woven fabric, metal foil (copper foil, aluminum foil), or composite material?
• Physical properties: how is the thickness, hardness, tensile strength, brittleness, elasticity?
• Surface characteristics: Is it smooth (easy to slide), is it coated (easy to scratch), is it easy to generate static electricity?
• Slitting requirements: slitting width accuracy, cutting edge requirements (smooth and burr-free or allow a little burr)?
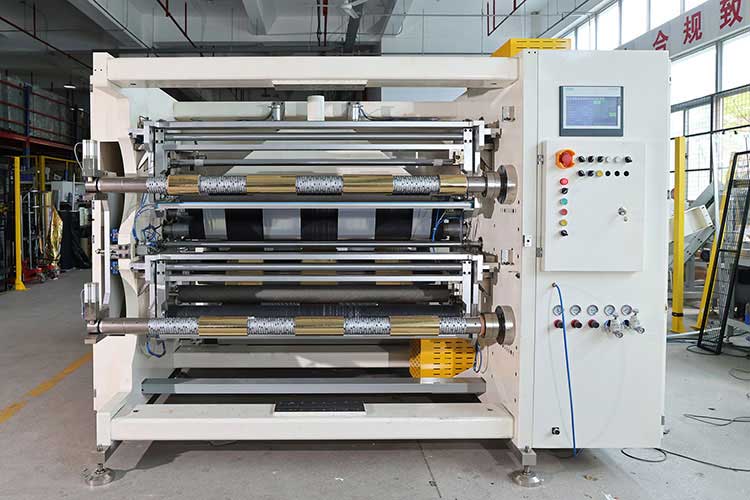

The second step to avoid pitfalls: take a seat in the right number, and choose different materials
1. General film, paper and non-woven fabrics
• Common materials:BOPP, CPP, PE, ordinary wrapping paper, coated paper, non-woven fabric for sanitary materials, etc.
• Core Challenge: Controlling tension to prevent stretch deformation and wrinkling; Ensure that the edges are cut neatly.
• Pit-avoidance selection suggestions:
◦ Tension control system: Choose a model equipped with a high-precision magnetic powder clutch or servo tension control system. The servo system is better and can realize taper tension control, especially suitable for easily stretched film materials.
◦ Slitting method: Circular knife slitting is preferred. For thinner materials, razor slitting (pad knife) is used, which is low cost and fast cutting effect; For slightly thicker or harder materials, use a circular knife cutter for slitting (upper and lower knife bite), which has better trim quality and longer life.
◦ Rewinding and unwinding configuration: The air expansion shaft can be equipped as standard, but its concentricity must be ensured to prevent uneven winding.
◦ Pitting avoidance point: Do not choose a model with unstable tension control to save costs, otherwise the slitted coil will be tight and loose on the outside, produce chrysanthemum patterns, and even become unusable.
2. High-precision, high value-added film and special paper
• Common materials:PET, BOPA, PI, lithium battery separator, high-end aluminized film, capacitive paper, etc.
• Core challenge: eliminate any scratches and indentations; Control of extremely small slitting width tolerances; Eliminates static electricity and dust.
• Pit-avoidance selection suggestions:
◦ Slitting method: You must use the Circular Knife Cutter Slitting. The material, angle and hardness of the blade are all extremely high, and it is recommended to choose imported alloy blades to ensure that the cut is smooth and smooth, without burrs and dust falling off.
◦ Contact part material: All guide rollers (over rollers) in contact with the material must be treated with high-precision dynamic balance, chrome or ceramic treatment on the surface to ensure smooth and flawless, and never use ordinary steel rollers.
◦ Tension control: A full servo tension control system must be used to achieve constant linear tension or taper tension control throughout the rewinding and unwinding coil, and the sensitivity is far supermagnetic powder clutch.
◦ Cleaning and static elimination: The equipment should be equipped with ion air rods and dust removal devices as standard to prevent static electricity from adsorbing dust and adhesion between membranes.
◦ Pitfalls: This is the area where you invest the most, but you get what you pay for. Any non-specialized configuration may result in product scrapping at a cost much higher than the equipment price difference.
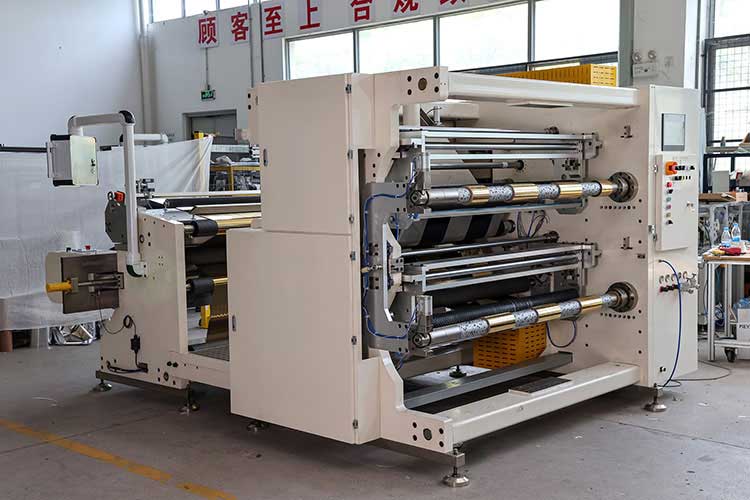

3. Metal foil (copper foil, aluminum foil)
• Common materials: copper foil and aluminum foil for lithium battery electrodes.
• Core challenges: metal foils are extremely thin (up to 6 μm), easy to break, easy to wrinkle, and easy to generate metal shavings.
• Pit-avoidance selection suggestions:
◦ Slitting method: Circular knife slitting is the only option, and the sharpness, wear resistance, and concentricity of the knife are extremely demanding. Special tool materials and edge designs are required.
◦ Tension control: requires extremely high tension control accuracy and stability, and a full servo system is standard. Slightly fluctuating tension can cause foil breakage or wrinkling.
◦ Dust Collection System: Critical! The metal shavings generated by slitting can directly affect battery performance. The equipment needs to be equipped with a powerful vacuum to remove debris immediately at the slitting point.
◦ Correction system: It must be equipped with a high-precision CCD or ultrasonic guidance system to ensure that the foil is always on the correct path during the slitting process and prevent waste caused by deviation.
◦ Pitfall avoidance point: This type of slitting machine is highly professional equipment, and should not be modified or replaced by ordinary film slitting machine. It is necessary to choose a supplier with mature cases and equipment experience in the field of lithium batteries.
4. Composite materials and thick materials
• Common materials: aluminum-plastic composite film, paper-aluminum-plastic composite film, woven fabric, leather, rubber mats, etc.
• Core challenges: uneven material thickness, high hardness, and high cutting resistance.
• Pit-avoidance selection suggestions:
◦ Slitting method: Heavy-duty circular knife slitting or straight knife slitting. For very hard materials, straight knife slitting (like a chisel cutter) may be a better choice, but it is slower. Circular knife slitting requires a strong rigid structure and drive horsepower.
◦ Rigidity of equipment: The frame of the whole machine must be strong and heavy to withstand huge slitting resistance to avoid vibration during work and affect the slitting quality.
◦ Tool material: Use heavy tools and consider the tool's cooling system to prevent annealing and accelerated wear due to overheating.
◦ Pit-avoidance point: Insufficient power and rigidity of equipment are the biggest hidden dangers. At best, it can be cut continuously, with serious burrs, and damage to the tool holder and spindle at worst.
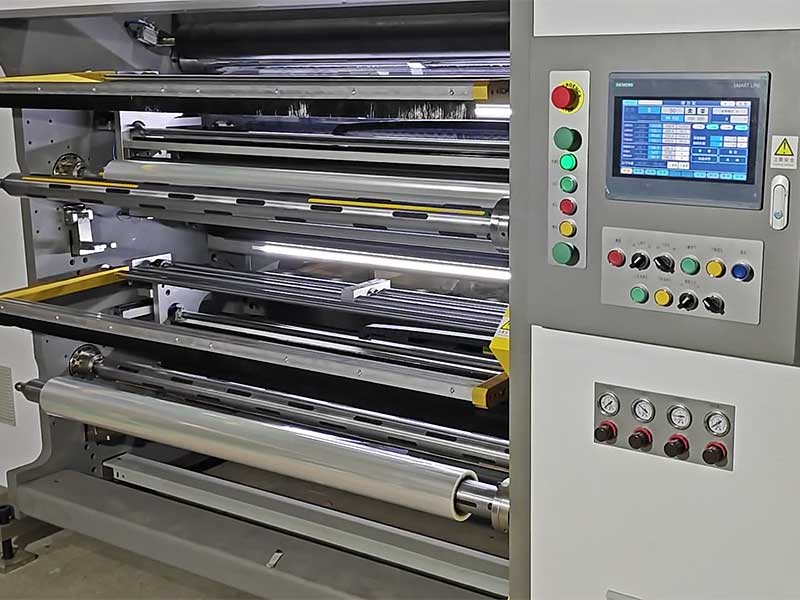

Summary: A list of pitfalls
Please make a final check against the following checklist before making a final decision:
1. Clarify the requirements: What is my material? What is the thinnest/thickest slit? What is the slitting accuracy required? What is the maximum roll diameter and width?
2. Core Configuration Check:
◦ Tension control: magnetic particle or servo? Does my material require servo-grade precision?
◦ Slitting method: round knife (razor/cutter) or straight knife? Which material is suitable for me?
◦ Tool quality: What is the tool material and brand? Is it easy to replace and grind?
◦ Equipment contact parts: Is the guide roller highly accurate and the surface treatment is appropriate?
3. Additional functions: Do you need automatic correction, dust removal, static elimination, and online defect detection?
4. Supplier inspection: Does the supplier have a successful case of similar materials to me? Can you provide trial service? Is the after-sales service timely?
Remember, the most expensive one may not be the most suitable, but the one that is far below the market price is almost always a "pit". Successful slitting machine selection stems from a deep understanding of their own processes and an accurate grasp of equipment performance. We hope this guide can help you clear the fog and choose the right model to protect your product quality and production efficiency.
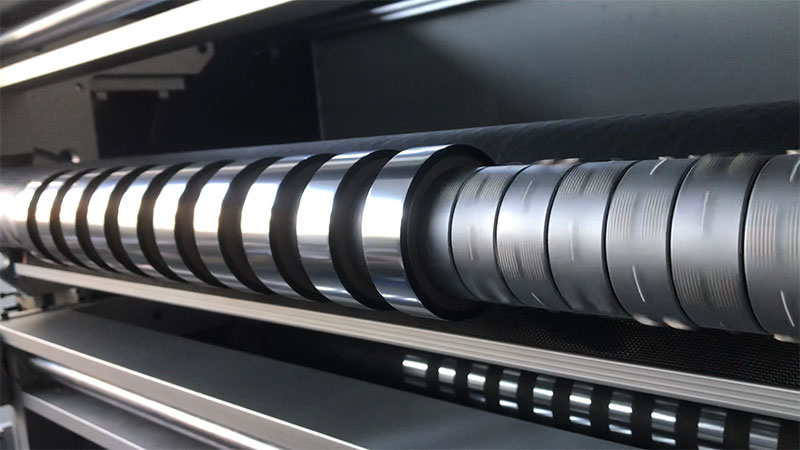
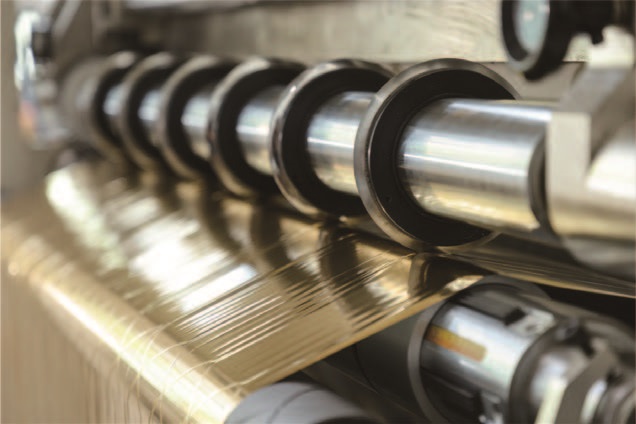





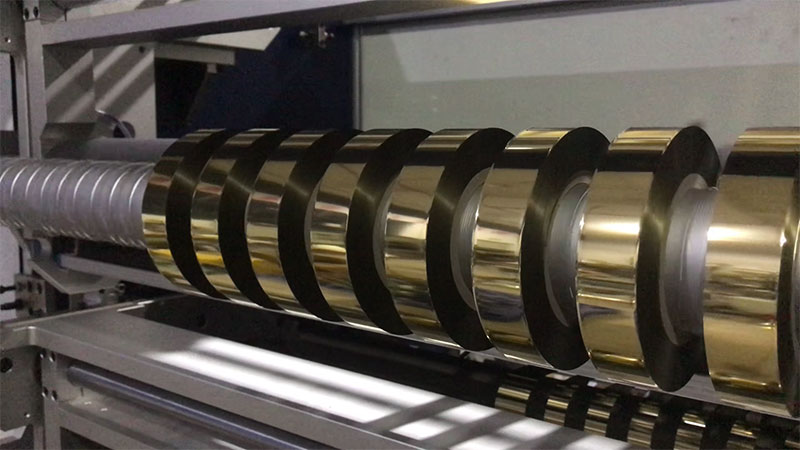

 Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus
Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts)
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts) Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus
Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus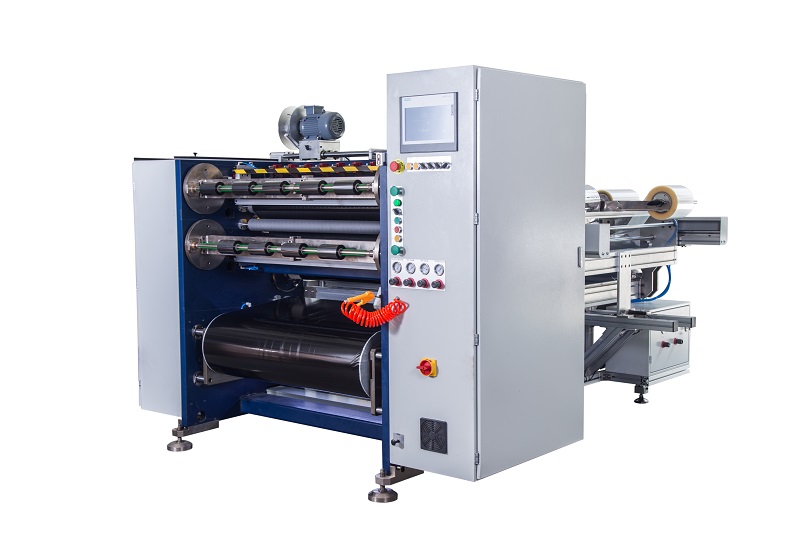 Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus
Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus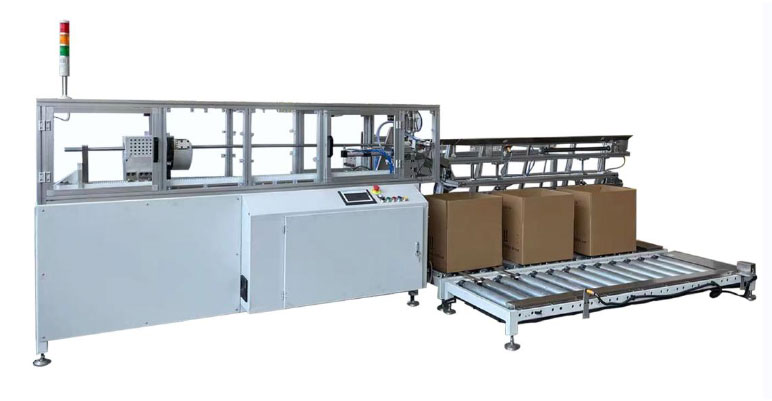 Auto Paper Core Cutter
Auto Paper Core Cutter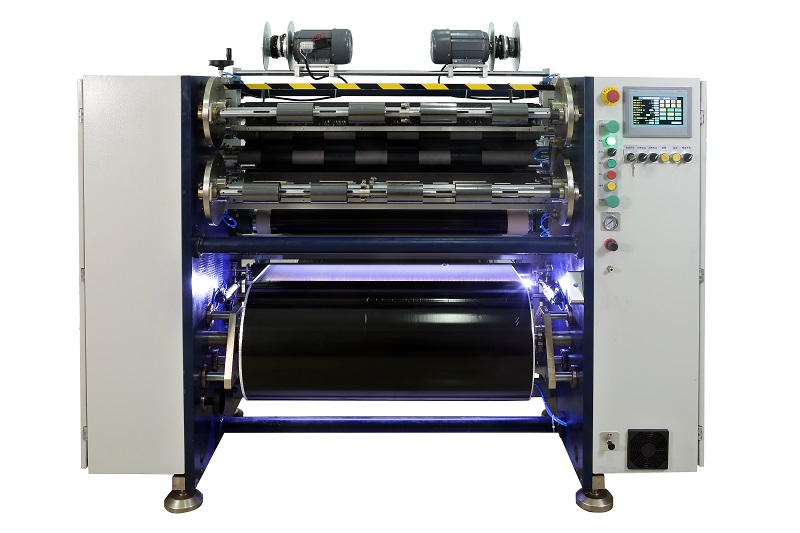 Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2
Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2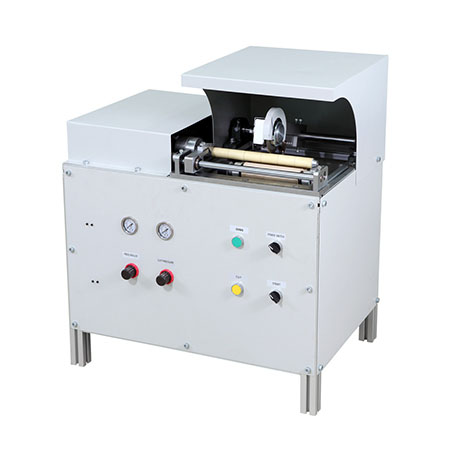 Manual Paper Core Cutter
Manual Paper Core Cutter