02. June, 2025delish0
When processing different ribbon types, the barcode ribbon slitting machine needs to achieve multi-material compatibility through hardware adaptation, process adjustment and intelligent control. Here's how to solve it:
1. Ribbon type identification and parameter preset
• Material Recognition System
Integrated optical sensor or RFID technology to automatically identify the ribbon type (wax-based/mixed/resin-based) and recall preset parameters (tension, temperature, speed, etc.).
• Database support
Establish a database of carbon strip material characteristics, including melting point, tensile strength, thickness, etc., to provide a basis for slitting parameters.
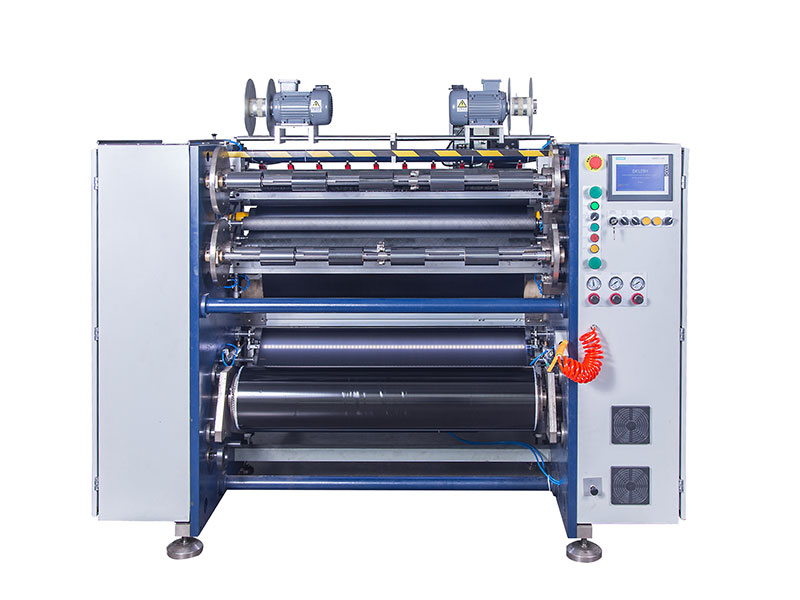

2. Adaptive design of the slitting core module
• Tension control system
◦ Dynamic adjustment: Closed-loop control of servo motor + tension sensor is used to adjust the tension in real time (5-10N for wax base and 15-30N for resin base).
◦ Anti-tensile design: Wax-based ribbons need low tension to avoid breakage, and resin-based ribbons need high tension to ensure flatness.
• Temperature management
◦ Slitting knife heating module: The resin-based ribbon needs to heat the blade (60-80°C) to reduce burrs, and the wax-based ribbon is slitted at room temperature.
◦ Constant environmental temperature: keep the temperature of the workshop stable (±2°C) to prevent thermal expansion and contraction from affecting the slitting accuracy.
• Tool selection and wear monitoring
◦ Multi-head configuration: high-frequency steel knives for soft wax bases, diamond-coated knives for high-hardness resin bases.
◦ Automatic knife grinding system: Detect the wear of the cutting edge by laser, trigger self-grinding or alarm replacement.
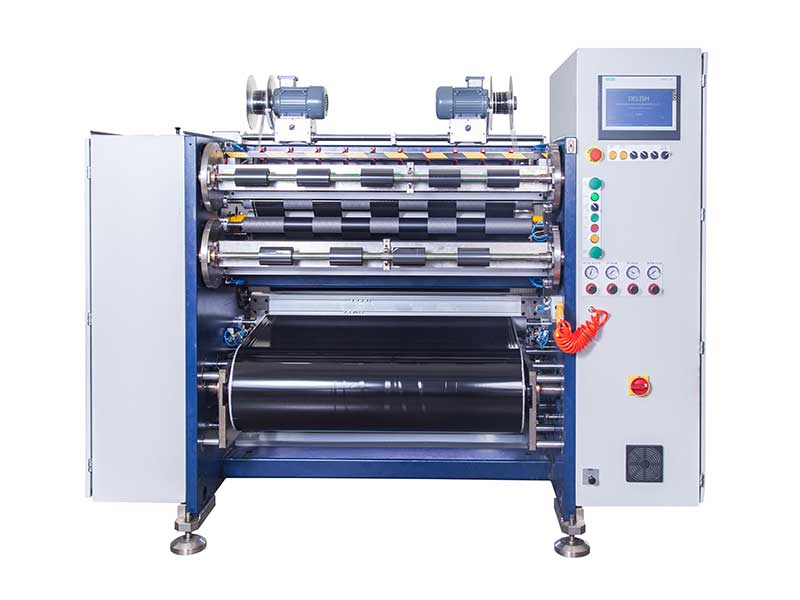

3. Slitting process optimization
• Speed matching
◦ Wax-based: high-speed slitting (150-200m/min), resin-based slowdown to 50-100m/min to reduce the risk of delamination.
• Winding strategy
◦ The taper winding technology is adopted, the initial tension is high, and the outer layer is gradually reduced to avoid the deformation of the ribbon (especially for thin base film PET material).
• Dust removal and lubrication
◦ Electrostatic precipitator is added during resin-based slitting, and micron-level lubricant is sprayed during wax-based slitting to reduce dust adhesion.
4. Intelligent and automated upgrades
• AI visual inspection
Real-time monitoring of slitting edge quality with automatic feedback adjustment parameters (if the resin-based carbon is found to have burrs, the speed is reduced and the knife temperature is increased).
• Adaptive learning
Train a machine learning model on historical data to optimize the combination of slitting parameters for different ribbons.
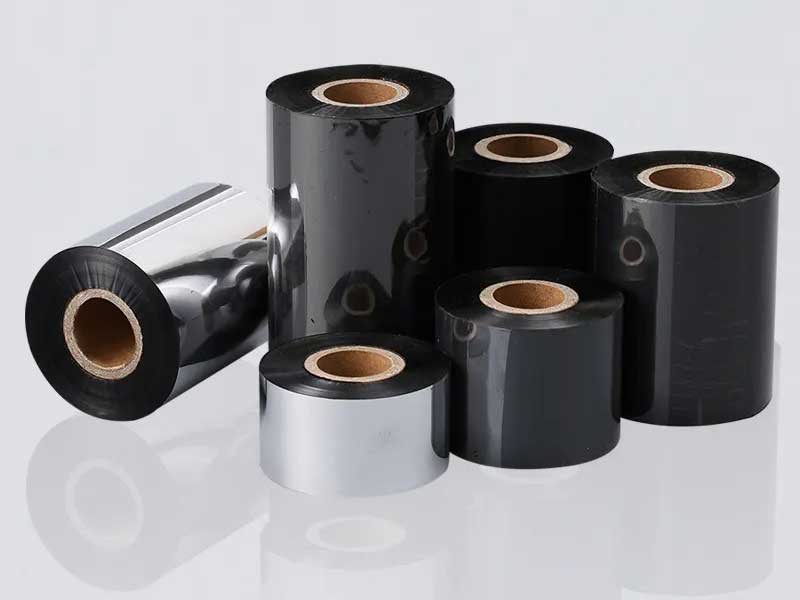

5. Special ribbon treatment scheme
• Multi-layer composite ribbons
Ultrasonic slitting technology is used to avoid interlayer peeling caused by traditional mechanical cutting.
• Ultra-thin ribbon (< 3μm)
The use of air-flotation guide rollers to reduce contact friction, combined with laser slitting to ensure edge uniformity.
6. Maintenance and calibration
• Periodic calibration
Calibrate the tension transducer and temperature probe weekly with an error of ±1%.
• Modular cleaning
Quick-disconnect knife sets and guide rollers to prevent cross-contamination of residual ribbon materials.
Through the above technical means, modern slitting machines can be compatible with more than 99% of ribbon types, the slitting accuracy is ±0.1mm, and the scrap rate can be reduced to less than 0.5%. The key is to translate material property data into machine control parameters and dynamically optimize them through a closed-loop system.





 Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus
Fully Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS8 Plus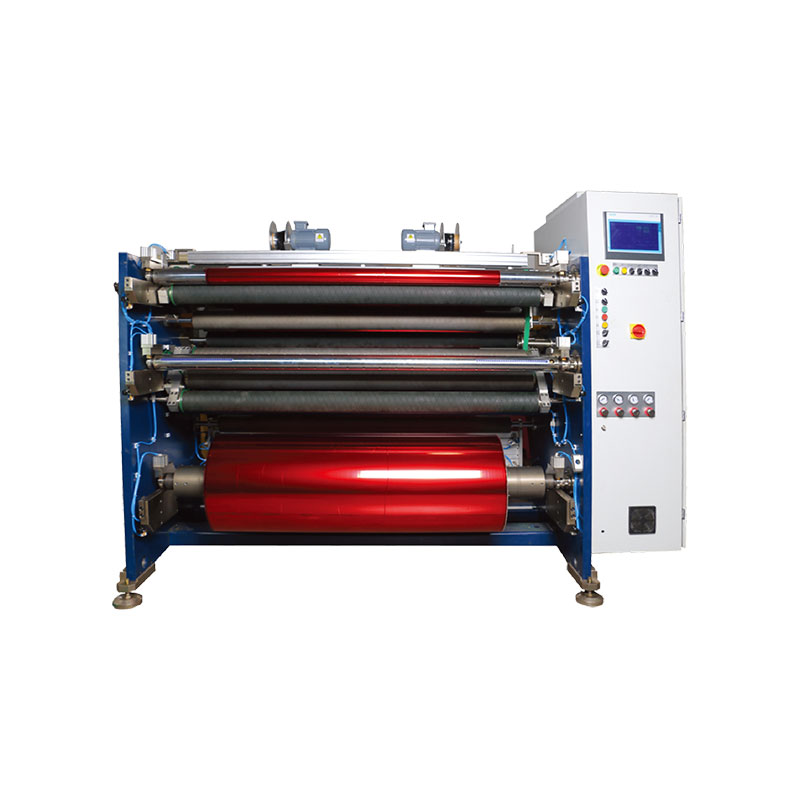 Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter 1600mm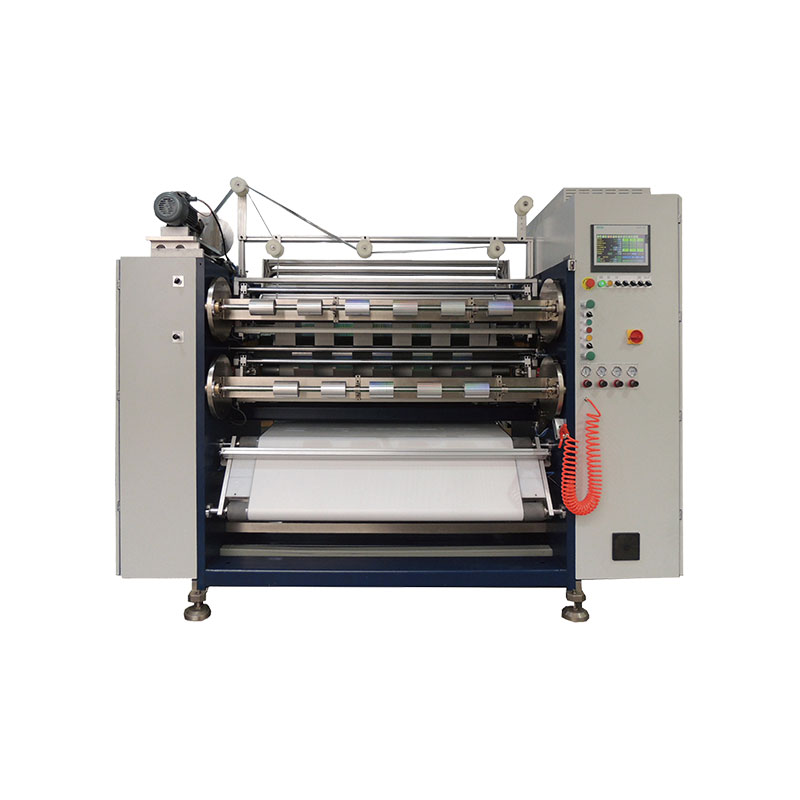 Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts)
Hot Stamping Foil Slitter (4 Shafts)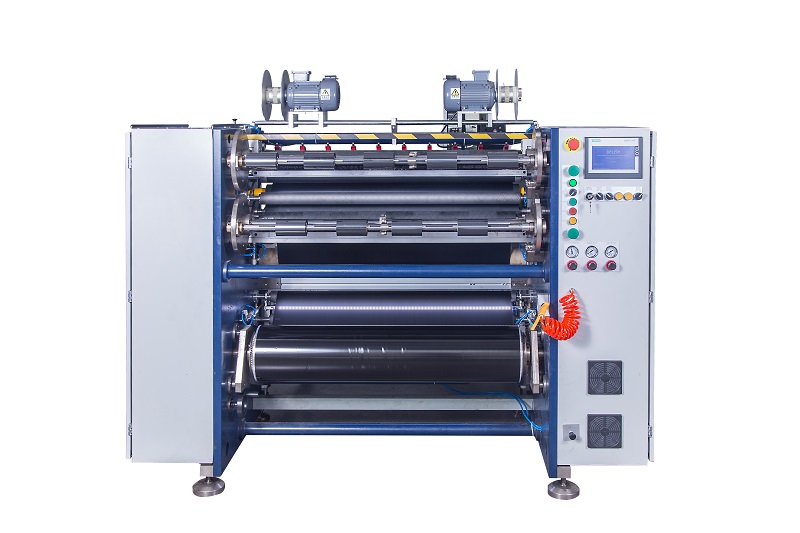 Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus
Semi-Auto TTR Slitter RSDS2 Plus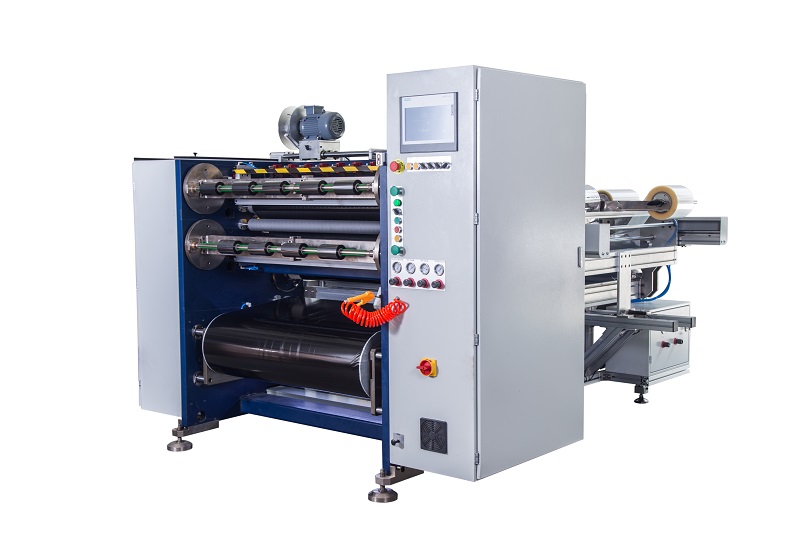 Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus
Semi Automatic TTR Slitter RSDS5 Plus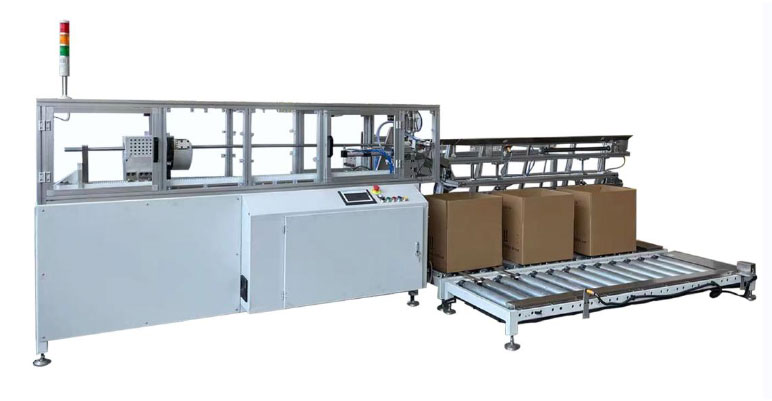 Auto Paper Core Cutter
Auto Paper Core Cutter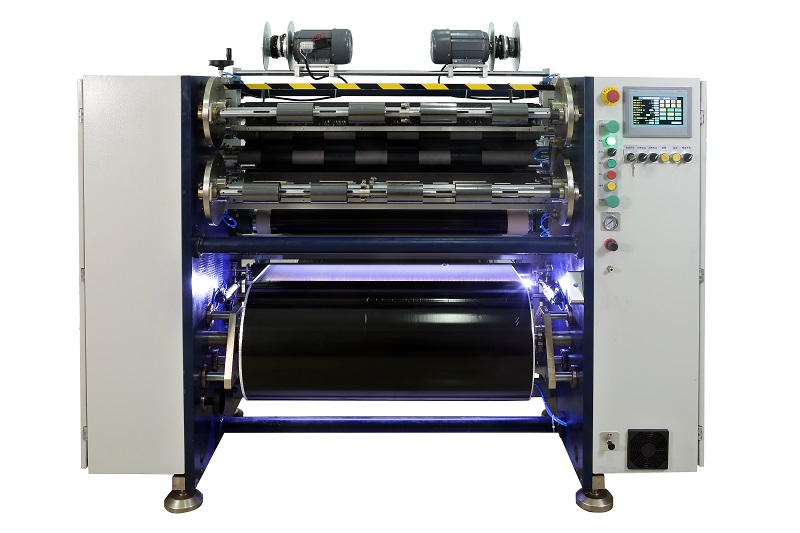 Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2
Manual TTR Slitter RSDS2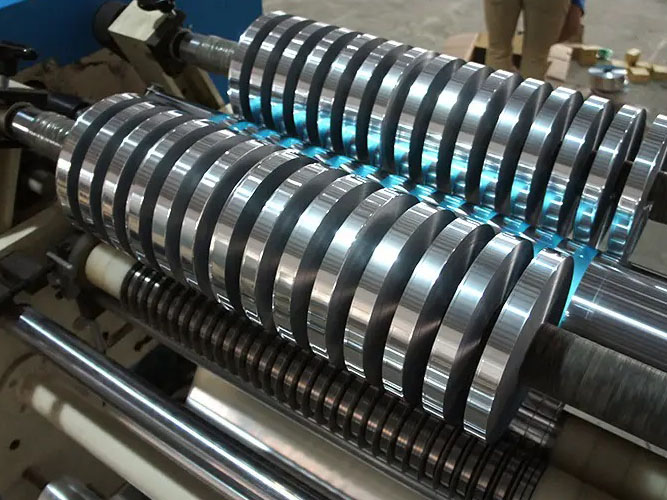 Aluminum Foil Slitting Machine
Aluminum Foil Slitting Machine